Upper Kuparuk River Region Vegetation
- Upper Kuparuk
- Vegetation
- SPOT
- Elevation
- Hydrology
- NDVI and Phytomass
- Landforms
- Glacial Geology
- Surficial Geology
- Surficial Geomorphology
- Literature
- Hierarchy of Geobotanical Vegetation Map Units (Walker DA 2002)
| Available data: | ||||
| |
GE |
Metadata |
GIS data |
GIS data |
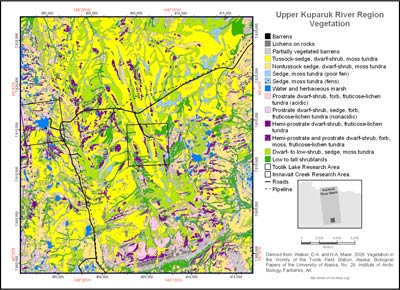
The vegetation of the region was studied and mapped as part of the Arctic Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) project at Toolik Lake and the Department of Energy R4D (Response, Resistance, Resilience and Recovery of vegetation from Disturbance) project at Imnavait Creek (Walker et al. 1994, Walker and Walker 1996). Fifty-seven plant communities and land-cover types were recognized during the mapping of the upper Kuparuk River region and are designated by the numeric GIS codes in the second column of the legend. These were grouped into the 14 physiognomic map units shown on Map A, which are compatible with the Circumpolar Arctic Vegetation Map (CAVM Team 2003) and the Alaska Arctic Tundra Vegetation Map (Raynolds et al. 2005, Raynolds et al. 2006).
- Barren
 1. Anthropogenic barren.
1. Anthropogenic barren.
Barren roads, gravel construction pads, airstrips and gravel mines.
270 ha, 0.4% of map 2. Lichens on rock.
2. Lichens on rock.
Bedrock and xeric blockfields.
1,009 ha, 1.3% of map 3. Partially vegetated barren.
3. Partially vegetated barren.
Partially vegetated barrens.
1,805 ha, 2.4% of map
- Moist Graminoid Tundra
 4. Tussock-sedge, dwarf-shrub, moss tundra.
4. Tussock-sedge, dwarf-shrub, moss tundra.
Mesic to subhygric, stable, acidic (pH < 5.5) sites with shallow to moderate snow. Flat areas and gentle slopes.
29,020 ha, 38.7% of map 5. Nontussock-sedge, dwarf-shrub, moss tundra.
5. Nontussock-sedge, dwarf-shrub, moss tundra.
Mesic to subhygric, nonacidic (pH > 5.5) sites with shallow to moderate snow. Flat areas and gentle slopes. Also miscellaneous graminoid-dominated sites including deep-snow stream margins, landslides and some rocky drained-lake basins.
13,153 ha, 17.5% of map
- Wet Graminoid Tundra and Water
 6. Sedge-moss tundra (poor fens).
6. Sedge-moss tundra (poor fens).
Subhydric to hydric, acidic (pH < 4.5). Poor fens, meadows in colluvial basins.
1,934 ha, 2.6% of map 7. Sedge-moss tundra (fens).
7. Sedge-moss tundra (fens).
Subhydric to hydric, nonacidic (pH > 4.5). Water tracks, stream margins, fens, flarks on solifuluction slopes.
1,160 ha, 1.5% of map 8. Water and herbaceous marsh.
8. Water and herbaceous marsh.
Hydric. Lakes, ponds and streams.
1,593 ha, 2.1% of map
- Prostrate-shrub tundra
 9. Prostrate dwarf-shrub, forb, fruticose-lichen tundra (acidic).
9. Prostrate dwarf-shrub, forb, fruticose-lichen tundra (acidic).
Xeric to xeromesic, acidic, wind blown to shallow winter snow cover. Ridge tops, exposed slopes, dry river terraces.
5,818 ha, 7.8% of map 10. Prostrate dwarf-shrub, sedge, forb, fruticose-lichen tundra (nonacidic).
10. Prostrate dwarf-shrub, sedge, forb, fruticose-lichen tundra (nonacidic).
Xeromesic to mesic, nonacidic. Includes a wide variety of drier nonacidic habitats, including stable river terraces and nonsorted stripes on slopes.
895 ha, 1.2% of map 11. Hemi-prostrate dwarf-shrub, fruticose-lichen tundra.
11. Hemi-prostrate dwarf-shrub, fruticose-lichen tundra.
Subxeric to mesic, acidic to nonacidic, with deep snow. Snowbeds.
2,164 ha, 2.9% of map 12. Hemi-prostrate and prostrate dwarf-shrub, forb, moss, fruticose-lichen tundra.
12. Hemi-prostrate and prostrate dwarf-shrub, forb, moss, fruticose-lichen tundra.
Subxeric to mesic, acidic to nonacidic, somewhat-deeper-snow areas. Depressions on acidic ridge crests, dry glacial till and outwash; nonsorted stripes.
2,116 ha, 2.8% of map
- Erect-shrub tundra
 13. Dwarf- to low-shrub, sedge, moss tundra.
13. Dwarf- to low-shrub, sedge, moss tundra.
Mesic to subhygric, moderate snow. Includes a wide variety of habitats with dwarf shrubs, including wet lower slopes, margins of upland water tracks, palsas and high-centered polygons.
9,045 ha, 12.1% of map 14. Low to tall shrublands.
14. Low to tall shrublands.
Mesic to subhydric, often with deep snow. Stream margins, upland water tracks and south-facing slopes.
5,344 ha, 7.1% of map


